

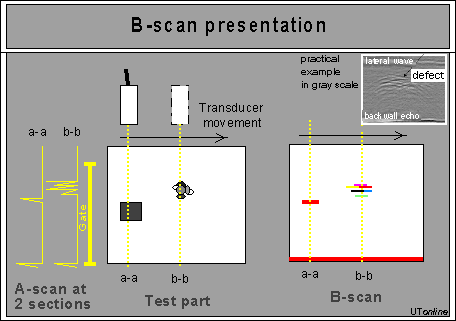
B-scan commonly used with conventional flaw detectors and corrosion thickness gages to plot the depth of reflectors with respect to their linear position. The thickness plotted as a function of time or position while the transducer scanned along the part to provide its depth profile.
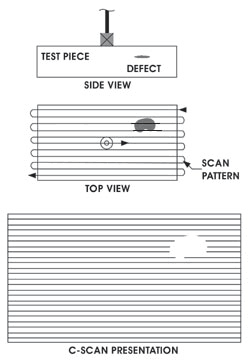
C-scan a two dimensional presentation of data displayed as a top or planar view of a test piece, similar in its graphic perspective to an x-ray image, where color represents the gated signal amplitude or depth at each point in the test piece mapped to its position. Planar images can be generated on flat parts by tracking data to X-Y position, or on cylindrical parts by tracking axial and angular position.
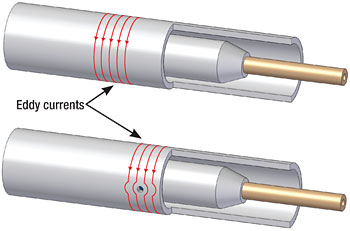
Eddy Current Non Destructive Testing is a reliable, quick and inexpensive way to carry out preventative maintenance and ensure safety.
In welding inspection there is a need to detect surface breaking defects. For magnetic material e.g. carbon steel, generally magnetic particle inspection is used. However, eddy current inspection offers a number of advantages:

Eddy Current Testing (ECT) is a noncontact method used to inspect non-ferromagnetic tubing. This technique is suitable for detecting and sizing metal discontinuities such as corrosion, erosion, wear, pitting, baffle cuts, wall loss, and cracks in nonferrous materials.
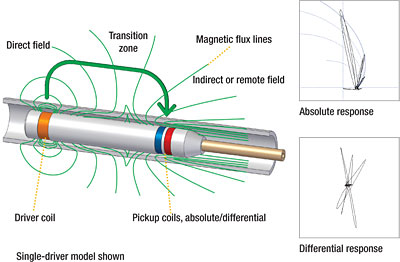
Remote Field Electromagnetic Testing (RFET) is being used to successfully inspect ferromagnetic tubing such as carbon steel or ferrite stainless steel. This technology offers good sensitivity when detecting and measuring volumetric defects resulting from erosion, corrosion, wear, and baffle cuts.
Magnetic flux leakage (MFL) is a fast inspection technique, suitable for measuring wall loss and detecting sharp defects such as pitting, grooving, and circumferential cracks. MFL is effective for aluminum-finned carbon steel tubes, because the magnetic field is almost completely unaffected by the presence of such fins.
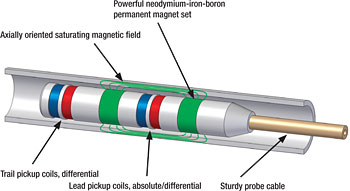
The ultrasonic IRIS option is used to inspect a wide range of materials, including ferrous, nonferrous, and non-metallic tubing. This technique detects and sizes wall loss resulting from corrosion, erosion, wear, pitting, cracking, and baffle cuts.
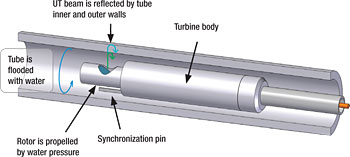
Eddy Current Tube Inspection is great for non ferrous tubing and provides rapid inspection compared to other types such as IRIS. ECT tube inspection can record and save tube data rapidly to then be analyzed by a technician at a later date.
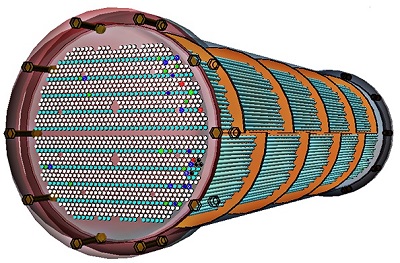
Acoustic Eye’s non-invasive solution for inner diameter inspection of today’s hard-to-inspect tubes up to 4″ enables ultra-fast, accurate inspection of boilers, Fin Fans and other heat exchangers regardless of tube shape or material.

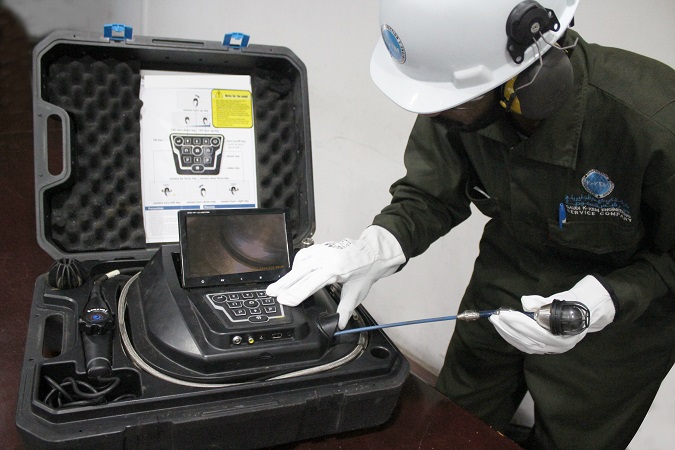
Borescopes are very useful for visual inspection work where the target area is inaccessible by other means, or where accessibility may require destructive, time consuming and/or expensive dismounting activities.
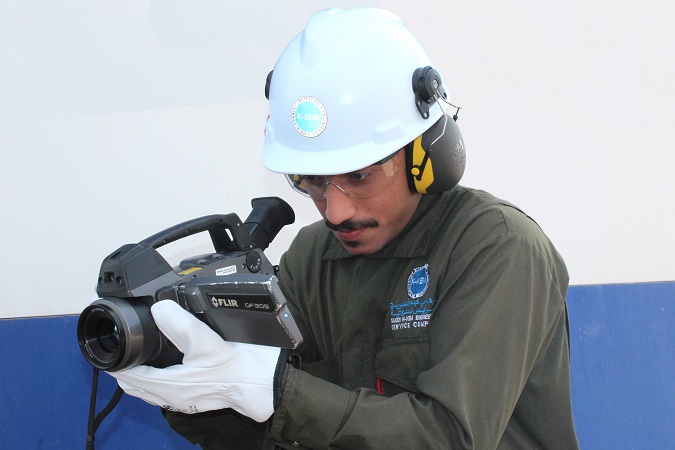


The GF309 is equipped with a special “flame filter” that allows you to see and measure high temperatures (up to +1500°C) through flames. Ideal for furnace and boiler inspections.
The FLIR GF309 visualizes temperatures from -20°C to +1,500°C. This makes the camera extremely suited for high temperature inspections.
The FLIR GF309 can be used both for internal and external furnace and maintenance inspections and can make also the smallest of temperature differences clearly visible.
A nickel coated heat shield improves worker safety and comfort during inspection.
The FLIR GF309 comes either with a fixed 14.5° lens or with a fixed 24° lens. A version with interchangeable lenses is also available but requires a US Department of State license.
The FLIR GF309 contains a cooled Indium Antimonite (InSb) detector. This highly sensitive detector is spectrally tuned to 3.8 – 4.05 micrometer waveband for seeing through flames.
SEEING IT THROUGH FLAMES The FLIR GF309 is an IR camera for the high-temperature measurement of industrial furnaces, chemical heaters, and coal-fired boilers, without the need to shut down the operation. The portable camera also greatly improves operator safety, by measuring through flames at a safe distance, for all types of furnaces. A good knowledge of the furnace condition can avert failures and unscheduled shutdowns.
Industrial furnaces, heaters, and boilers are found in the chemical, petrochemical, and utility industries.
Handheld XRF analyzers provide fast, accurate chemistry and alloy identification in PMI applications including piping, valves, welds, components, and pressure vessels. Vanta analyzers are essential for:

Radiography is a well-established conventional NDT technique with inherent risks associated with the use of radiation. Managing the safety risk by the setting of ‘controlled areas’ has the adverse effect of reducing clients’ production time. It was this clear market pull that triggered the innovative capability of Oceaneering to develop the ‘Small Controlled Area Radiography’ (SCAR) system. The system enables radiography to be performed in the heart of the workplace without disruption to normal operations.
SCAR-a directional gamma radiography system for use in areas congested with workers, confined spaces, or where radiation output must be kept to an absolute minimum so not to disrupt normal operations.
SCAR has been developed with safety and productivity as the main objectives, and has simply set the precedent for safer radiography in the industry.

Short Range Ultrasonic testing – SRUT is a screening non-destructive test method to detect corrosion on the pipe wall or plates concealed under support structures or structural shell.
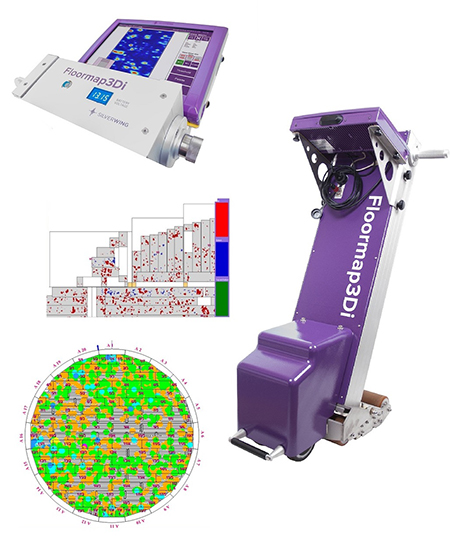
The Floormap combines two distinct technologies, MFL and STARS. The introduction of STARS (Surface topology air-gap reluctance sensors) enables the scanner to determine whether there is corrosion top side, bottom side or below the surface coating.
Improved signal to noise ratio combined with STARS and MFL ensures a more accurate and efficient inspection of coated and thicker plates.
The RMS2 is a high speed, high accuracy remote access ultrasonic corrosion mapping system designed to evaluate the condition of assets as storage tanks, pipelines, pressure vessels and other critical equipment, supporting efficient inspection programme that support integrity management processes to ensure effective and safe operation.
The RMS2 ultrasonic scanner can give 100% coverage in a band up to 1000 mm wide, significantly increasing Probability of Detection (POD) of defects and corrosion, enabling engineers to determine the optimum repair strategy and improve remaining life assessment (RLA) & risk based inspection (RBI) maintenance programs.
The RMS2 is extremely flexible with a range of scanning heads to suit different inspection requirements.

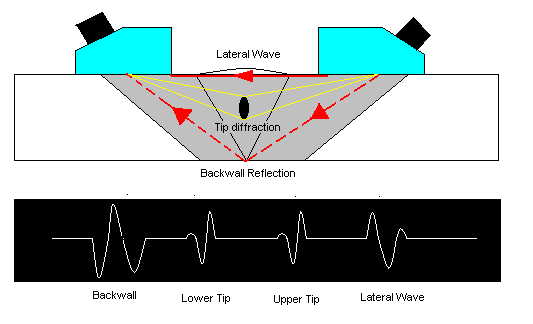
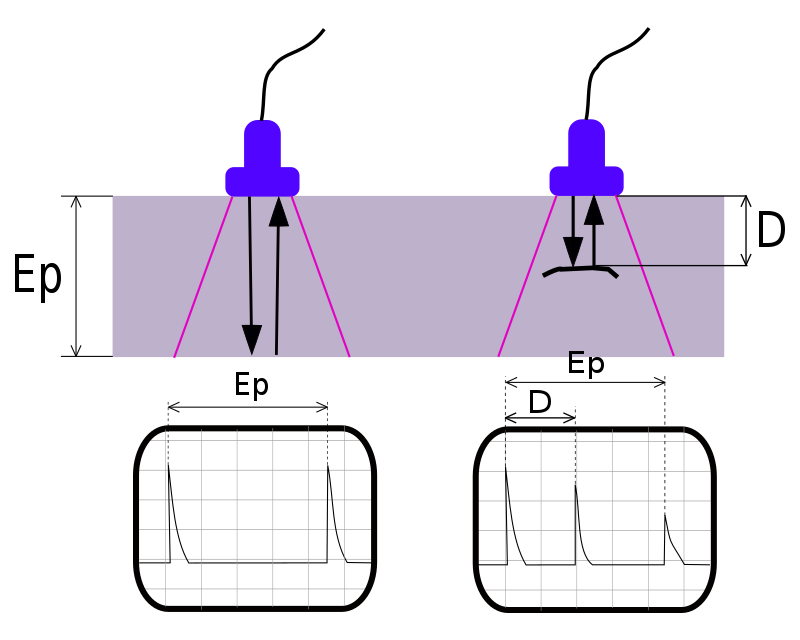
Time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD) method of ultrasonic testing is a sensitive and accurate method for the nondestructive testing of welds for defects.
Measuring the amplitude of reflected signal is a relatively unreliable method of sizing defects because the amplitude strongly depends on the orientation of the crack. Instead of amplitude, TOFD uses the time of flight of an ultrasonic pulse to determine the position and size of a reflector.
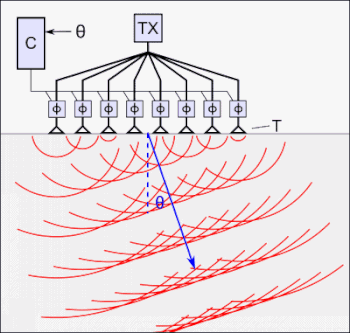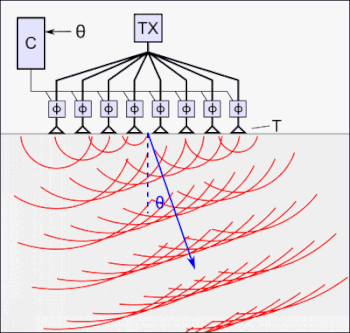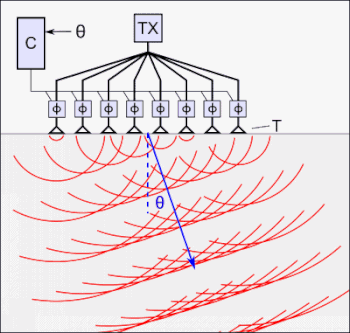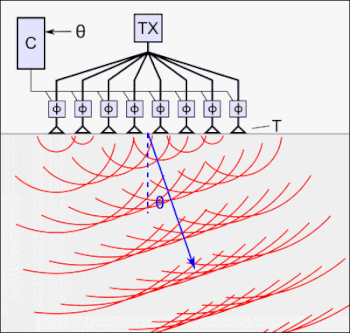
Phased array ultrasonics testing (PAUT) is an advanced method of ultrasonic testing that has applications in industrial nondestructive testing. This method is an advanced NDT method that is used to detect discontinuities i.e. cracks or flaws and thereby determine component quality. Due to the possibility to control parameters such as beam angle and focal distance, this method is very efficient regarding the defect detection and speed of testing.[1] Apart from detecting flaws in components, phased array can also be used for wall thickness measurements in conjunction with corrosion testing.[2][3] Phased array can be used for the following industrial purposes:

Guided wave testing (GWT) is a non-destructive evaluation method. The method employs acoustic waves that propagate along an elongated structure while guided by its boundaries. This allows the waves to travel a long distance with little loss in energy. Nowadays, GWT is widely used to inspect and screen many engineering structures, particularly for the inspection of metallic pipelines around the world. In some cases, hundreds of meters can be inspected from a single location. There are also some applications for inspecting rail tracks, rods and metal plate structures.
This test method is suitable for leak detection on pipes, containers and sheet metal structures.
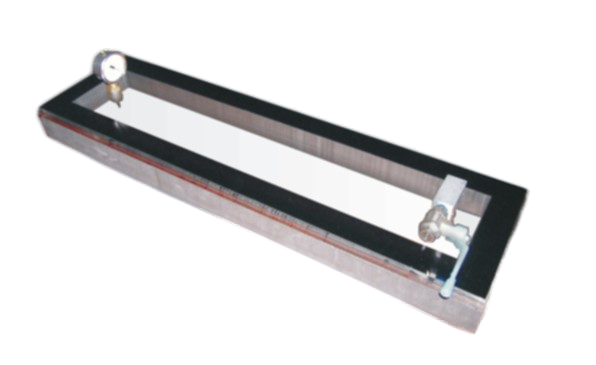
The objective of the vacuum box technique is to locate leaks in a pressure boundary that cannot be directly pressurized. This is accomplished by applying a soapy solution to a local area of the pressure boundary surface and creating a differential pressure across that local area of the boundary.
Holiday testing is a non-destructive test method applied on protective coatings to detect unacceptable discontinuities such as pinholes and voids. The test involves checking an electric circuit to see if current flows to complete the circuit. This testing is used to find coating film discontinuities that are not readily visible.
The testing is usually performed on tank interiors, chemical storage vessels and buried structures because of the importance of maintaining adequate coating protection in aggressive service environments.
